As you know HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. In a nutshell, it destroys the T-cells that your body needs. Over time, HIV can develop into AIDS — especially untreated — and be fatal.
15 Common Symptoms of HIV
Symptoms can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks. During this time, HIV infection may not show up on some types of HIV tests, but people who have it are highly infectious and can spread the infection to others. If you need to find a testing location, use this HIV Testing Sites & Care Services Locator to find a site near you.
About 40 percent to 90 percent of people have flu-like symptoms within 2-4 weeks after HIV infection. Other people do not feel sick at all during this stage, which is also known as acute HIV infection. Early infection is defined as HIV infection in the past six months (recent) and includes acute (very recent) infections.

1. Fever
When your body has an infection, one of the early symptoms is a fever, which also occurs after an HIV infection.

2. Fatigue
After being infected with HIV, your body attempts to fight off the virus. You might feel weak, fatigued and/or out of breath.
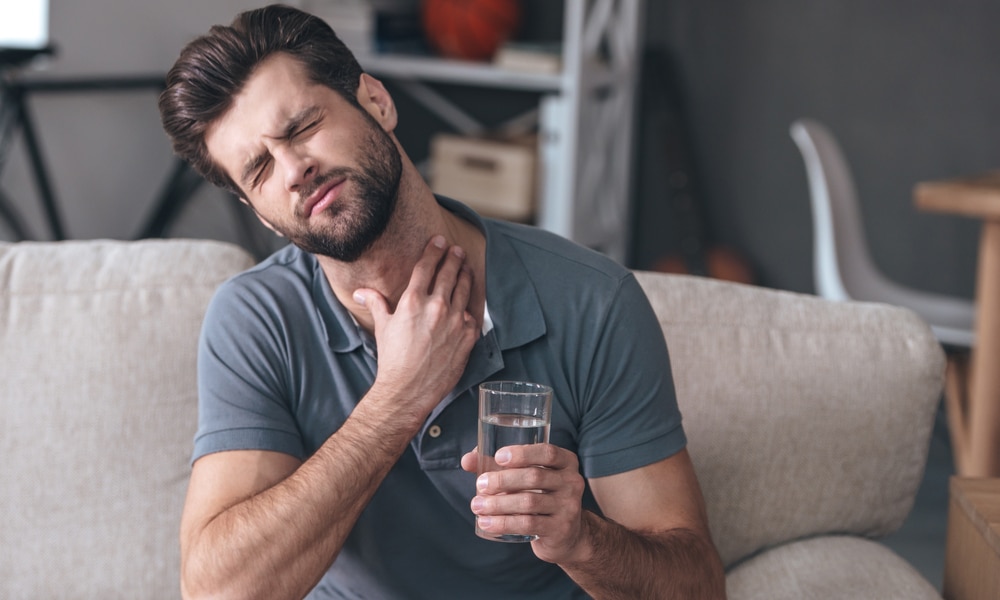

3. Swollen or enlarged lymph nodes
The lymph nodes in your neck, arm pit or groin will swell as your body reacts to the virus.
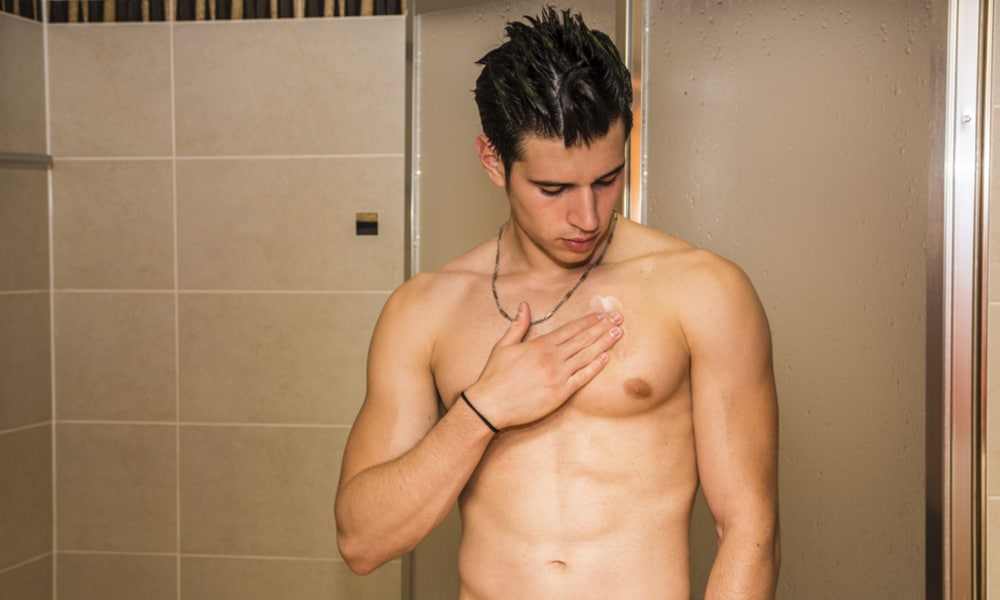

4. Rash
While less common, a rash can appear on your body. It’s appearance varies, so if you have an unexplained rash, see your doctor ASAP.
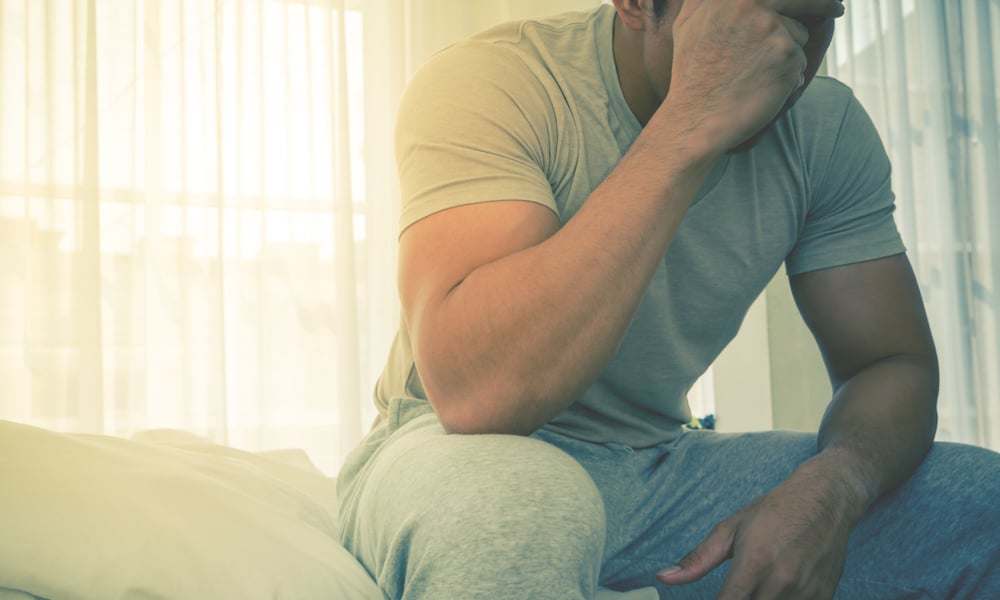

5. Myalgia
The muscles in your body will feel achy or painful — like the aches and pains associated with having the flu.
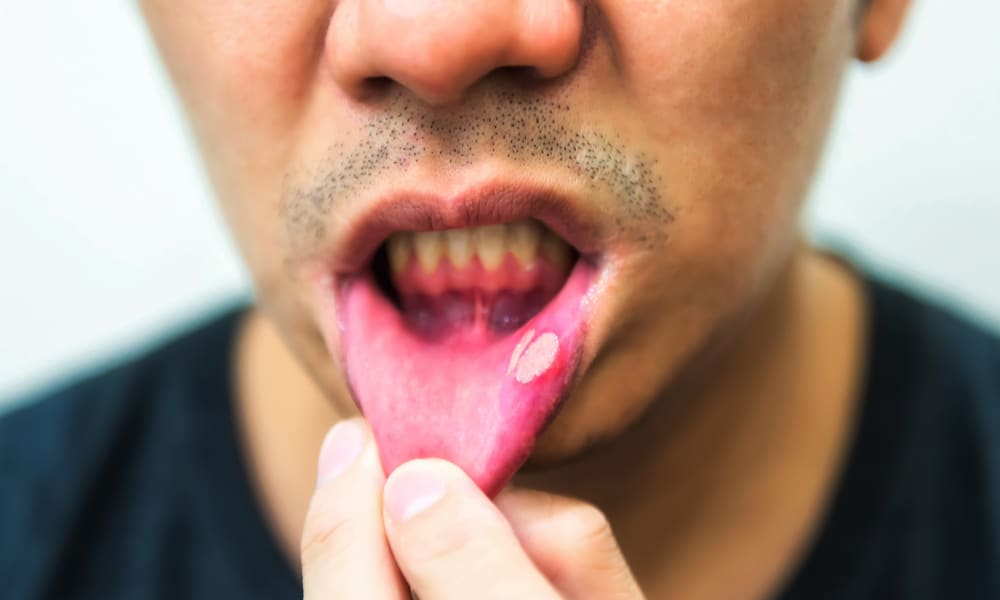
6. Mouth sores
Open sores can develop on your mouth and throat, as well as your junk.
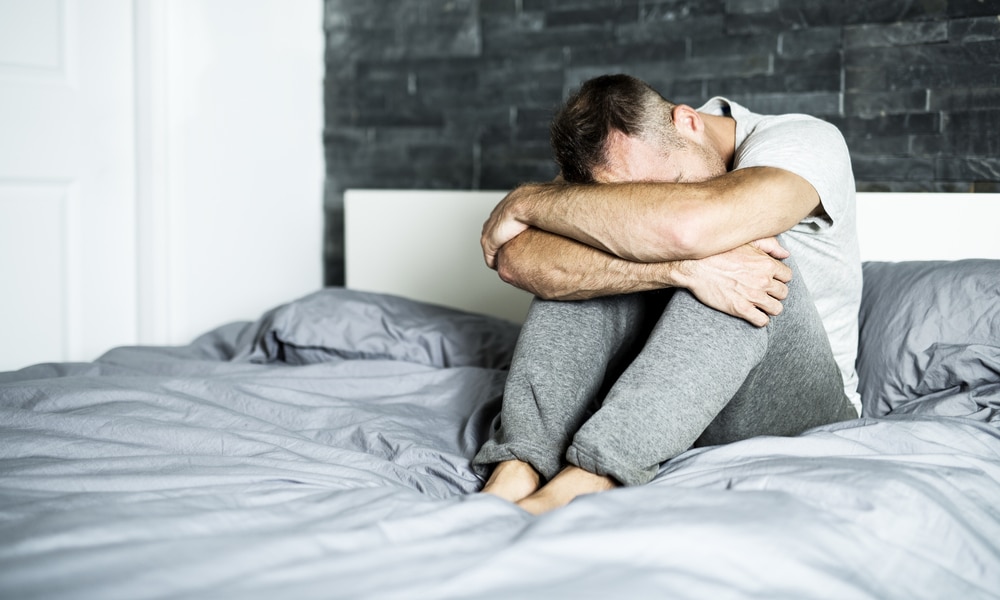

7. Feeling uneasy
Some people intuitively know that something is wrong, and will feel extremely anxious and uneasy.
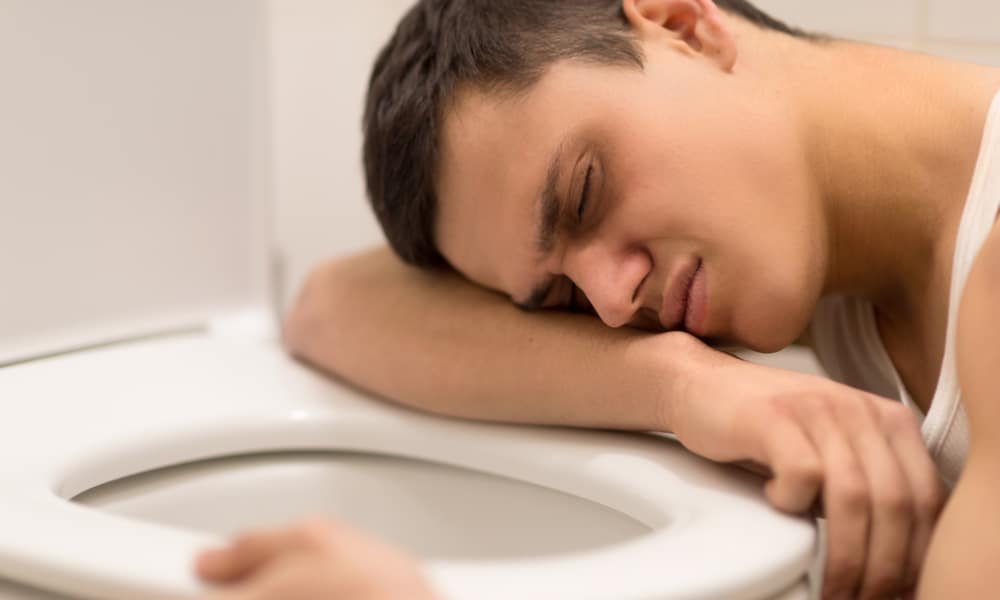

8. Nausea/vomiting
If you’ve been recently infected with HIV, you might feel nauseated, which can result in vomiting.
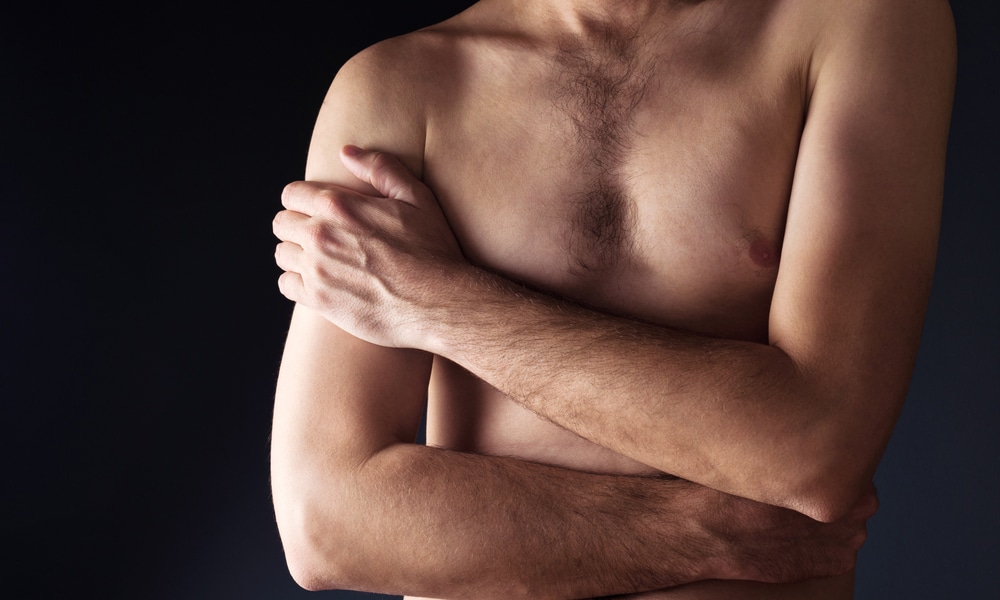

9. Weight loss
Due to the lack of appetite and vomiting, weight loss is likely to occur.
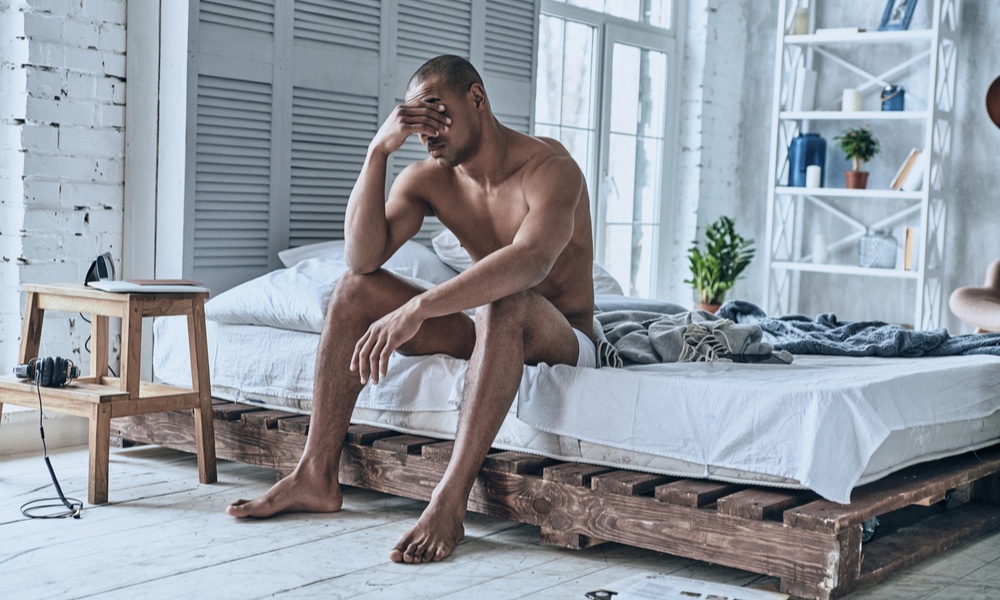

10. Headache
Having a persistent and throbbing headache could happen, too.
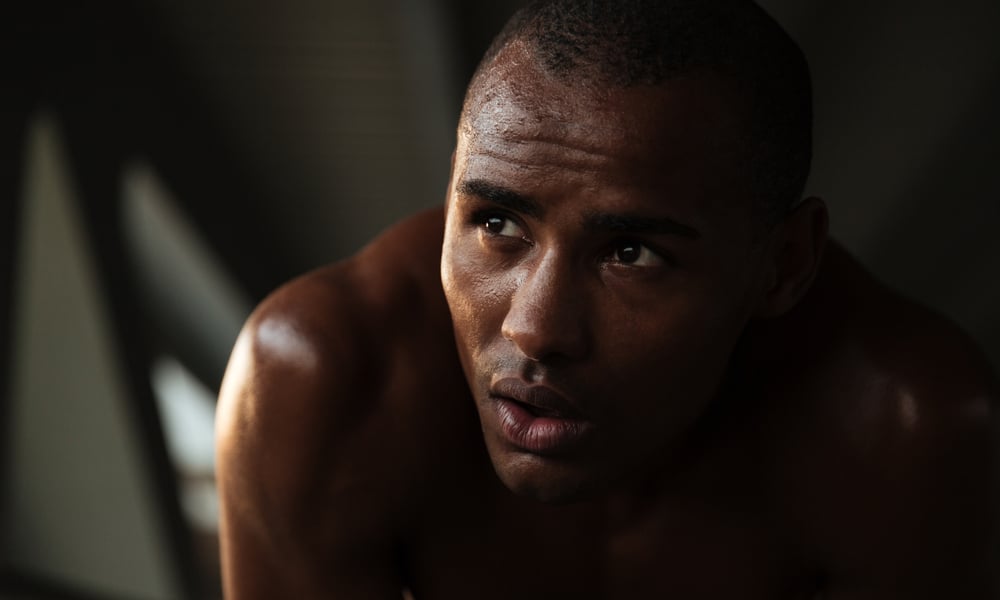

11. Night sweats
Waking up to drenched sheets is usually associated with latent symptoms.
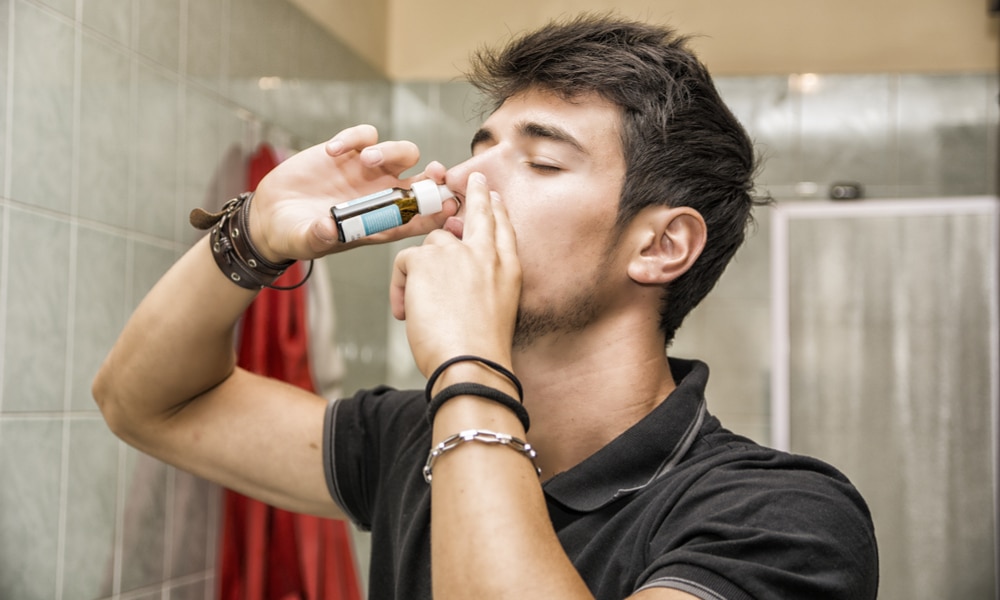

12. Nasal Congestion
Feeling congested or stuffed up can be another sign of a recent infection.
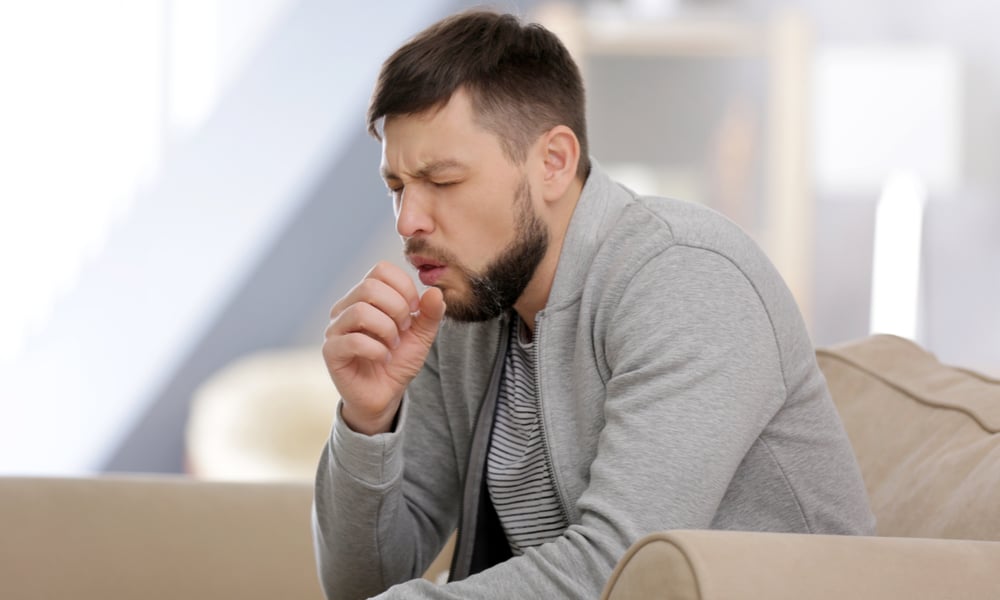

13. Dry cough
You know the feeling of a hacking cough? It’s sort of like that, but more intense.
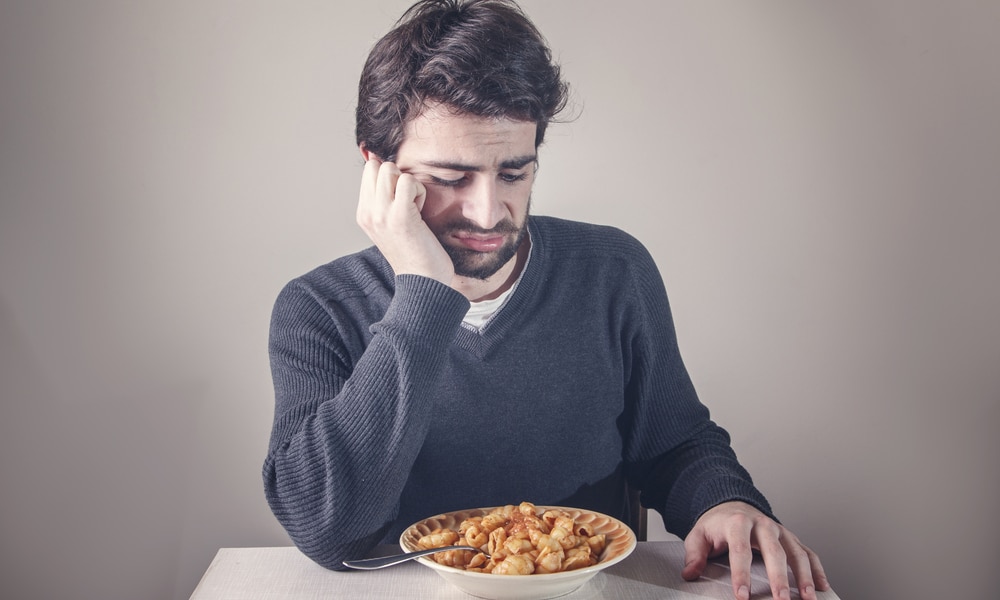

14. Lack of appetite
With nausea and diarrhea, it is common that you may lose your desire to eat.
15. Shortness of breath
You’re not able to catch your breath, which makes it really hard to exercise and complete your daily routine.
The only way to know your HIV status is through HIV testing. But there are HIV symptoms that might motivate you to get tested. Knowing your status is important because it helps you make healthy decisions to prevent getting or transmitting HIV.
How Can I Tell if I Have HIV?
You should not assume you have HIV just because you have any of the symptoms listed above. Each of these symptoms can be caused by other illnesses, and some people who have HIV do not show any symptoms for 10 years or more.
However, if you think you may have been exposed to HIV and could be in the early stage of HIV infection, get an HIV test. Most HIV tests detect antibodies (proteins your body makes as a reaction against the presence of HIV), not HIV itself. But it take can take a few weeks or longer for your body to produce these antibodies.
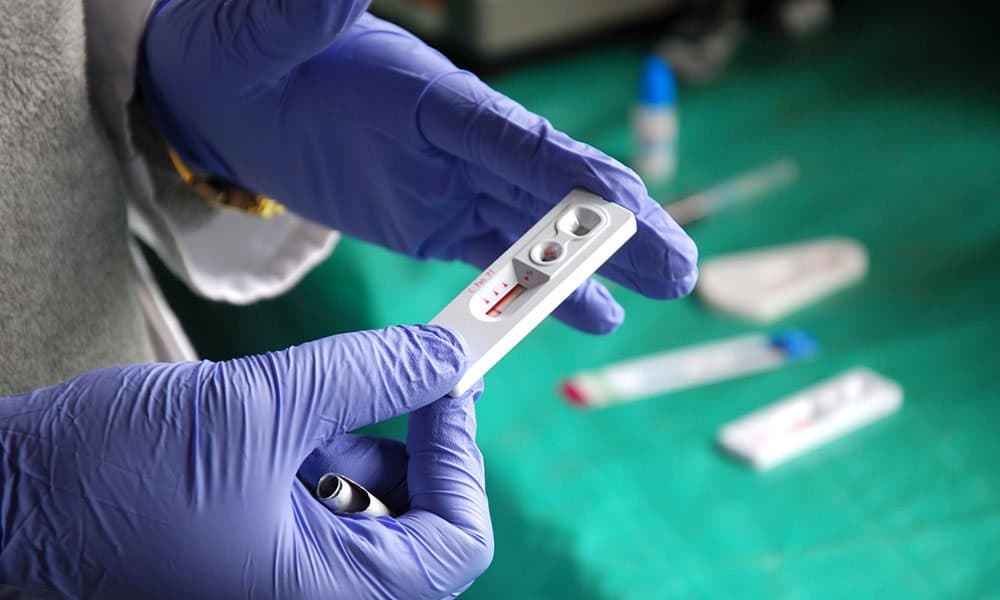
How to Get Tested for HIV
If you’re uncomfortable going into a testing facility, you can test yourself at home. We recommend the myLAB Box at Home STD Test or Oraquick; both options are discreet and allow you to test for HIV from the comfort of your home. If you’d prefer to test in a facility, you have many options.
Some places use HIV tests that can detect acute and recent infections, but others do not. So be sure to let your testing site know if you think you may have been recently infected with HIV. Tests that can detect acute infection look for HIV RNA or p24 antigen. Most doctors and clinics that provide a full range of health care services can do this test, but some places that only do HIV testing may not have it. So you may want to contact the site before you go to ask if they can test you for acute HIV infection.
After you get tested, it’s important to find out the result of your test. If you’re HIV-positive, you should see a doctor and start HIV treatment as soon as possible. You are at high risk of transmitting HIV to others during the early stage of HIV infection, even if you have no symptoms. For this reason, it is very important to take steps to reduce your risk of transmission. If you’re HIV-negative, explore HIV-prevention options, like pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), that can help you stay negative.
Related | Take an HIV Test From Home With myLAB Box
After an HIV infection, many people experience acute retroviral syndrome (ARS) 2-4 weeks after contact with HIV. If you have some of the symptoms above, don’t panic. The virus affects everyone’s body differently, and some symptoms don’t apply to each HIV case. If you’re having sex, protect yourself and know your status.

